The emergence of the internet has transformed how we shop and access goods, but it has also introduced a hidden realm known as the dark web. Within this shadowy corner of the internet, dark web markets flourish, offering an variety of illicit products and services that are often just a click away. These markets operate outside the reach of standard regulatory frameworks, creating an environment where anonymity and secrecy prevail.
As e-commerce continues to lead the worldwide marketplace, understanding the dynamics of these underground markets becomes increasingly important. They reveal not just the shadowy aspects of consumer behavior but also the challenges faced by law enforcement and policymakers. By investigating how dark web markets function, we can gain insights into the complexities of modern commerce and the ever-evolving landscape of online transactions.
Comprehending the Shadowy Web
The dark web denotes a section of the internet that is not cataloged by conventional search engines, making it a concealed space reachable solely through particular software, configurations, or permissions. The predominant method of accessing the dark web is through the Tor service, which masks users' personal information and activity. This environment draws in a mix of individuals searching for privacy, including informants, activists, and those participating in criminal activities.
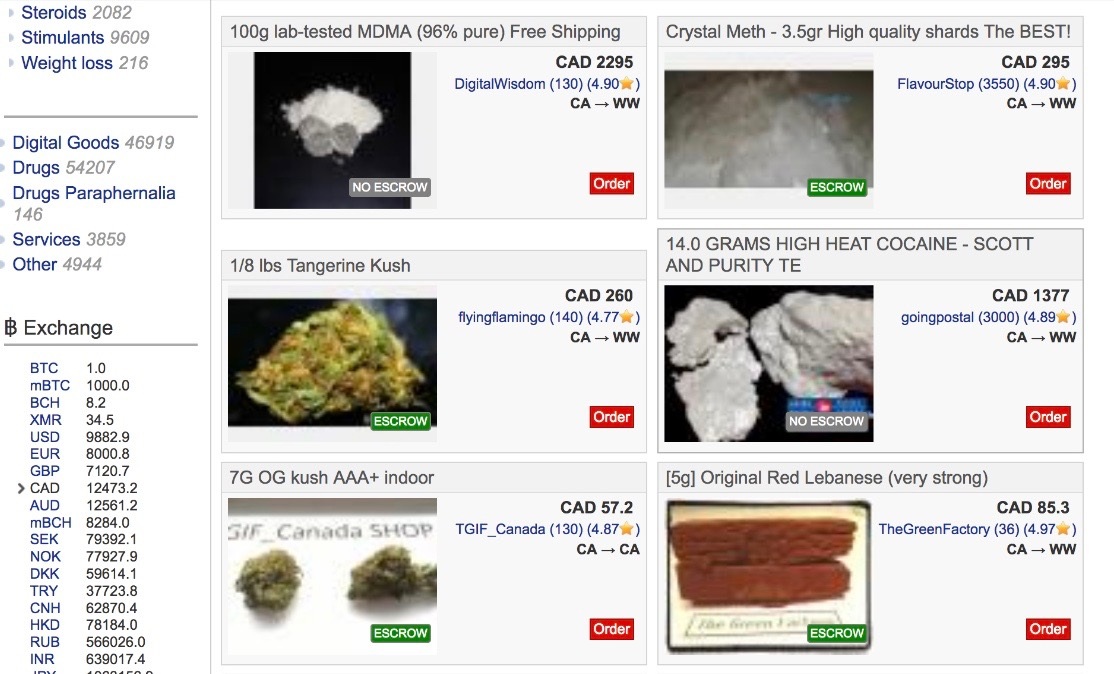
Within the dark web, a range of marketplaces operate, offering goods and services that can span the benign to the highly illegal. These markets commonly accept cryptocurrencies, adding an additional layer of anonymity. Users can buy a wide array of products, including forbidden drugs, fake currency, hacking services, and stolen data. This anonymity, while a positive aspect for many, creates serious issues regarding safety, legality, and moral considerations.
The architecture of the dark web is constructed to foster privacy and security, which can lead to both beneficial and negative outcomes. While it offers a refuge for those needing anonymity, such as reporters reporting in oppressive regimes, it also serves as a haven for criminal activities. Understanding this duality is vital to grasping the complex dynamics that define dark web markets and their impact on society at large.
Systems of Dark Web Markets
Dark web markets operate on the principle of secrecy, utilizing tools and strategies that help preserve the identities of both consumers and merchants. The usual method of accessing these markets is through custom software like Tor, which hides user addresses and encrypts communications. This anonymity is a double-edged sword as it draws in not just legitimate privacy supporters but also criminals seeking to purchase or trade illicit goods and offerings. The marketplace environments are often constructed to mimic standard online shopping websites, making it simpler for users to move through and finalize transactions.
Transaction methods in dark web markets typically lean on cryptocurrencies, with BTC being the most widely used. These digital currency exchanges provide an additional layer of security, as they can be challenging to follow. Merchants may set up an escrow system to confirm that payments are only disbursed once the customer verifies receipt of the items. This trust mechanism is vital in an atmosphere where traditional consumer rights regulations do not exist. Vendors may also cultivate reputations through feedback from buyers, akin to user reviews on popular websites, which helps signal trustworthiness and quality among the broad and often tumultuous listings.

Deception and scams are common in darknet markets, as the lack of control creates a breeding ground for dishonesty. Participants face dangers from both dishonest sellers and police. To reduce these dangers, many markets employ protections, such as mandating users to participate in community forums for verification and adopting multi-signature systems to increase security of transactions. As darknet markets continue to change, new approaches of functioning are appearing, adapting to changes in tech and enforcement tactics, thus perpetuating a intricate cycle of advancement and illicit transactions. darkmarket list
Risks and Ethical Implications
Participating with dark web markets presents substantial risks, both buyers and vendors. The secrecy that these platforms offer can be alluring, but it also fosters a hazardous environment where scams and fraud are prevalent. Users may discover themselves becoming targets to counterfeit goods or being cheated out of their money without means of recourse. Additionally, the risk of legal repercussions is significant, as many transactions involve illicit goods and services that can lead to stringent penalties if caught by law enforcement.
Ethically, the existence of dark web markets raises serious concerns. The sale of illegal substances, arms, and stolen data does not just challenge the legality of such transactions but also contributes to societal harm. These markets can sustain addiction, violence, and theft, which impacts individuals and communities equally. Furthermore, the secrecy provided can numb individuals to the moral implications of their purchases, resulting in a disconnect between action and consequence.
Moreover, the dark web is instrumental in encouraging a culture of cybercrime that extends past simple consumer transactions. It enables the exchange of knowledge and tools that can be used for harmful purposes, such as hacking and identity theft. This environment reinforces a cycle in which crime becomes accessible and even normalized, raising deep ethical questions about personal responsibility and the impact of technology on human behavior. The duality of anonymity versus accountability presents continuing challenges for both society as a whole.
